About the AgriMet Network
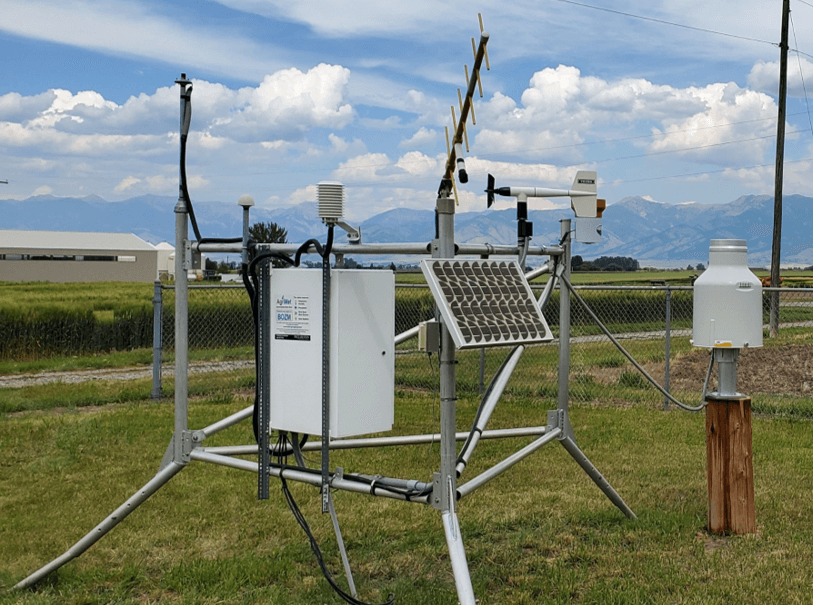
The Missouri Basin and Arkansas-Rio Grande-Texas Gulf AgriMet network began in 1989 as an extension of the Columbia - Pacific Northwest AgriMet network, which began collecting data in 1983. The term "AgriMet" is a contraction of "Agriculture" and "Meteorology", emphasizing the network's focus on collecting real-time weather data from farms and agricultural areas. AgriMet operates on top of Reclamation's existing "HydroMet" network, which stores and processes hydrologic data such as channel flows, reservoir levels, and river stages.
AgriMet data is used to estimate crop-specific evapotranspiration, allowing irrigators to estimate thier crop-water usage. By applying the right amount of water at the right time, irrigators can maximize yields and minimize water and power consumption.
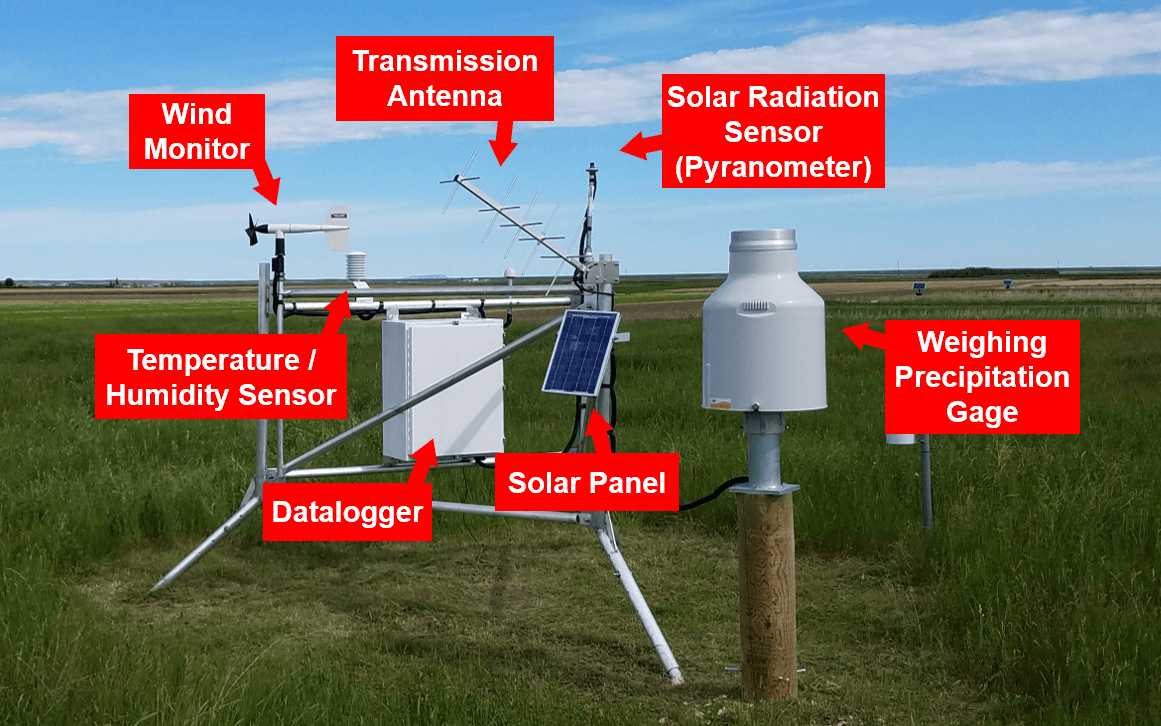
Sensors at AgriMet stations record the following weather parameters:
- 15-minute peak wind gust
- 15-minute average temperature
- 15-minute average humidity
- 15-minute average dew-point temperature
- 1-hour accumulated precipitation
- 1-hour accumulated solar radiation
- 1-hour average wind speed
AgriMet also reports on daily statistics, including:
- Daily mean, max, and min temperature
- Daily mean humidity
- Daily mean dewpoint temperature
- Daily solar radiation
- Daily precipitation
- Daily average wind speed
- Daily max wind gust
- Daily Kimberly-Penman evapotranspiration
- Growing Degree Days
Some AgriMet stations also collect soil moisture and soil temperature data at 2", 4", 8", 20", and 40" depths.
For further information about AgriMet, contact: mbwebmaster.

